Code Quality (STARTER)
Introduced in GitLab Starter 9.3.
With the help of GitLab CI/CD, you can analyze your source code quality using GitLab Code Quality.
Code Quality:
- Uses Code Climate Engines, which are free and open source. Code Quality doesn't require a Code Climate subscription.
- Runs in pipelines using an Docker image built in GitLab Code Quality project.
- Can make use of a template.
- Is available with Auto DevOps.
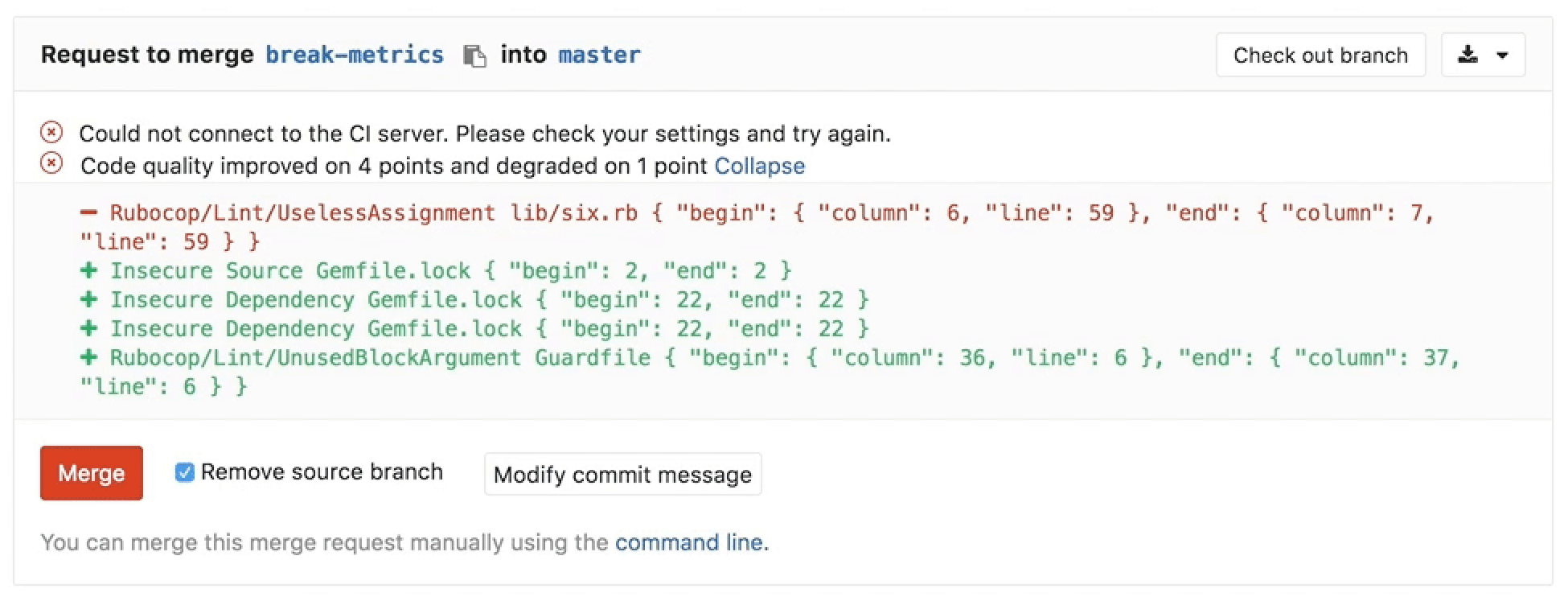
Going a step further, GitLab can show the Code Quality report right in the merge request widget area:
Use cases
For instance, consider the following workflow:
- Your backend team member starts a new implementation for making a certain feature in your app faster.
- With Code Quality reports, they analyze how their implementation is impacting the code quality.
- The metrics show that their code degrade the quality in 10 points.
- You ask a co-worker to help them with this modification.
- They both work on the changes until Code Quality report displays no degradations, only improvements.
- You approve the merge request and authorize its deployment to staging.
- Once verified, their changes are deployed to production.
Example configuration
CAUTION: Caution: The job definition shown below is supported on GitLab 11.11 and later versions. It also requires the GitLab Runner 11.5 or later. For earlier versions, use the previous job definitions.
This example shows how to run Code Quality on your code by using GitLab CI/CD and Docker.
First, you need GitLab Runner with docker-in-docker executor.
Once you set up the Runner, include the CodeQuality template in your CI config:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.ymlThe above example will create a code_quality job in your CI/CD pipeline which
will scan your source code for code quality issues. The report will be saved as a
Code Quality report artifact
that you can later download and analyze. Due to implementation limitations we always
take the latest Code Quality artifact available.
It is also possible to override the URL to the Code Quality image by
setting the CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE variable. This is particularly useful if you want
to lock in a specific version of Code Quality, or use a fork of it:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
variables:
CODE_QUALITY_IMAGE: "registry.example.com/codequality-fork:latest"By default, report artifacts are not downloadable. If you need them downloadable on the
job details page, you can add gl-code-quality-report.json to the artifact paths like so:
include:
- template: Code-Quality.gitlab-ci.yml
code_quality:
artifacts:
paths: [gl-code-quality-report.json]The included code_quality job is running in the test stage, so it needs to be included in your CI config, like so:
stages:
- testTIP: Tip: This information will be automatically extracted and shown right in the merge request widget.
CAUTION: Caution: On self-managed instances, if a malicious actor compromises the Code Quality job definition they will be able to execute privileged docker commands on the Runner host. Having proper access control policies mitigates this attack vector by allowing access only to trusted actors.
Previous job definitions
CAUTION: Caution:
Before GitLab 11.5, Code Quality job and artifact had to be named specifically to
automatically extract report data and show it in the merge request widget. While these
old job definitions are still maintained they have been deprecated and may be removed
in the next major release, GitLab 12.0. You are advised to update your current .gitlab-ci.yml
configuration to reflect that change.
For GitLab 11.5 and later, the job should look like:
code_quality:
image: docker:stable
variables:
DOCKER_DRIVER: overlay2
allow_failure: true
services:
- docker:stable-dind
script:
- export SP_VERSION=$(echo "$CI_SERVER_VERSION" | sed 's/^\([0-9]*\)\.\([0-9]*\).*/\1-\2-stable/')
- docker run
--env SOURCE_CODE="$PWD"
--volume "$PWD":/code
--volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
"registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/codequality:$SP_VERSION" /code
artifacts:
reports:
codequality: gl-code-quality-report.jsonIn GitLab 12.6, Code Quality switched to the
new versioning scheme.
It is highly recommended to include the Code Quality template as shown in the
example configuration, which uses the new versioning scheme.
If not using the template, the SP_VERSION variable can be hardcoded to use the
new image versions:
code_quality:
image: docker:stable
variables:
DOCKER_DRIVER: overlay2
SP_VERSION: 0.85.6
allow_failure: true
services:
- docker:stable-dind
script:
- docker run
--env SOURCE_CODE="$PWD"
--volume "$PWD":/code
--volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
"registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/codequality:$SP_VERSION" /code
artifacts:
reports:
codequality: gl-code-quality-report.jsonFor GitLab 11.4 and earlier, the job should look like:
code_quality:
image: docker:stable
variables:
DOCKER_DRIVER: overlay2
allow_failure: true
services:
- docker:stable-dind
script:
- export SP_VERSION=$(echo "$CI_SERVER_VERSION" | sed 's/^\([0-9]*\)\.\([0-9]*\).*/\1-\2-stable/')
- docker run
--env SOURCE_CODE="$PWD"
--volume "$PWD":/code
--volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
"registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/codequality:$SP_VERSION" /code
artifacts:
paths: [gl-code-quality-report.json]Alternatively the job name could be codeclimate or codequality and the artifact
name could be codeclimate.json. These names have been deprecated with GitLab 11.0
and may be removed in the next major release, GitLab 12.0.
For GitLab 10.3 and earlier, the job should look like:
codequality:
image: docker:latest
variables:
DOCKER_DRIVER: overlay
services:
- docker:dind
script:
- docker pull codeclimate/codeclimate:0.69.0
- docker run --env CODECLIMATE_CODE="$PWD" --volume "$PWD":/code --volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --volume /tmp/cc:/tmp/cc codeclimate/codeclimate:0.69.0 init
- docker run --env CODECLIMATE_CODE="$PWD" --volume "$PWD":/code --volume /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --volume /tmp/cc:/tmp/cc codeclimate/codeclimate:0.69.0 analyze -f json > codeclimate.json || true
artifacts:
paths: [codeclimate.json]Configuring jobs using variables
The Code Quality job supports environment variables that users can set to configure job execution at runtime.
For a list of available environment variables, see Environment variables.
Implementing a custom tool
It's possible to have a custom tool provide Code Quality reports in GitLab. To do this:
- Define a job in your
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile that generates the Code Quality report artifact. - Configure your tool to generate the Code Quality report artifact as a JSON file that implements subset of the Code Climate spec.
The Code Quality report artifact JSON file must contain an array of objects with the following properties:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
description |
A description of the code quality violation. |
fingerprint |
A unique fingerprint to identify the code quality violation. For example, an MD5 hash. |
location.path |
The relative path to the file containing the code quality violation. |
location.lines.begin |
The line on which the code quality violation occurred. |
Example:
[
{
"description": "'unused' is assigned a value but never used.",
"fingerprint": "7815696ecbf1c96e6894b779456d330e",
"location": {
"path": "lib/index.js",
"lines": {
"begin": 42
}
}
}
]NOTE: Note: Although the Code Climate spec supports more properties, those are ignored by GitLab.
Code Quality reports
Once the Code Quality job has completed, GitLab:
- Checks the generated report.
- Compares the metrics between the source and target branches.
- Shows the information right on the merge request.
If multiple jobs in a pipeline generate a code quality artifact, only the artifact from the last created job (the job with the largest job ID) is used. To avoid confusion, configure only one job to generate a code quality artifact.
If the Code Quality report doesn't have anything to compare to, no information
will be displayed in the merge request area. That is the case when you add the
Code Quality job in your .gitlab-ci.yml for the very first time.
Consecutive merge requests will have something to compare to and the Code Quality
report will be shown properly.