Reviewing and managing merge requests
Merge requests are the primary method of making changes to files in a GitLab project. Changes are proposed by creating and submitting a merge request, which is then reviewed, and accepted (or rejected).
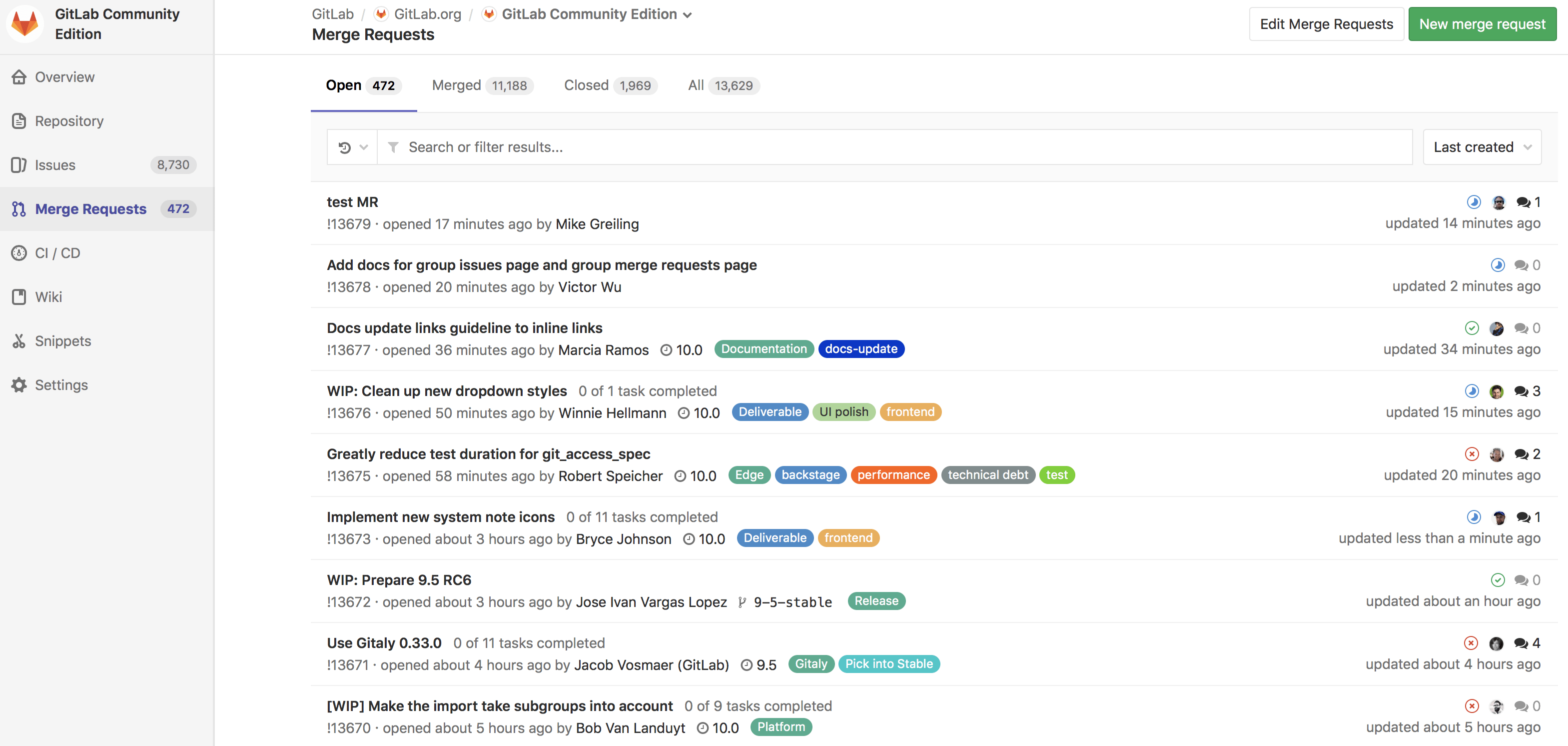
View project merge requests
View all the merge requests within a project by navigating to Project > Merge Requests.
When you access your project's merge requests, GitLab will present them in a list, and you can use the tabs available to quickly filter by open and closed. You can also search and filter the results.
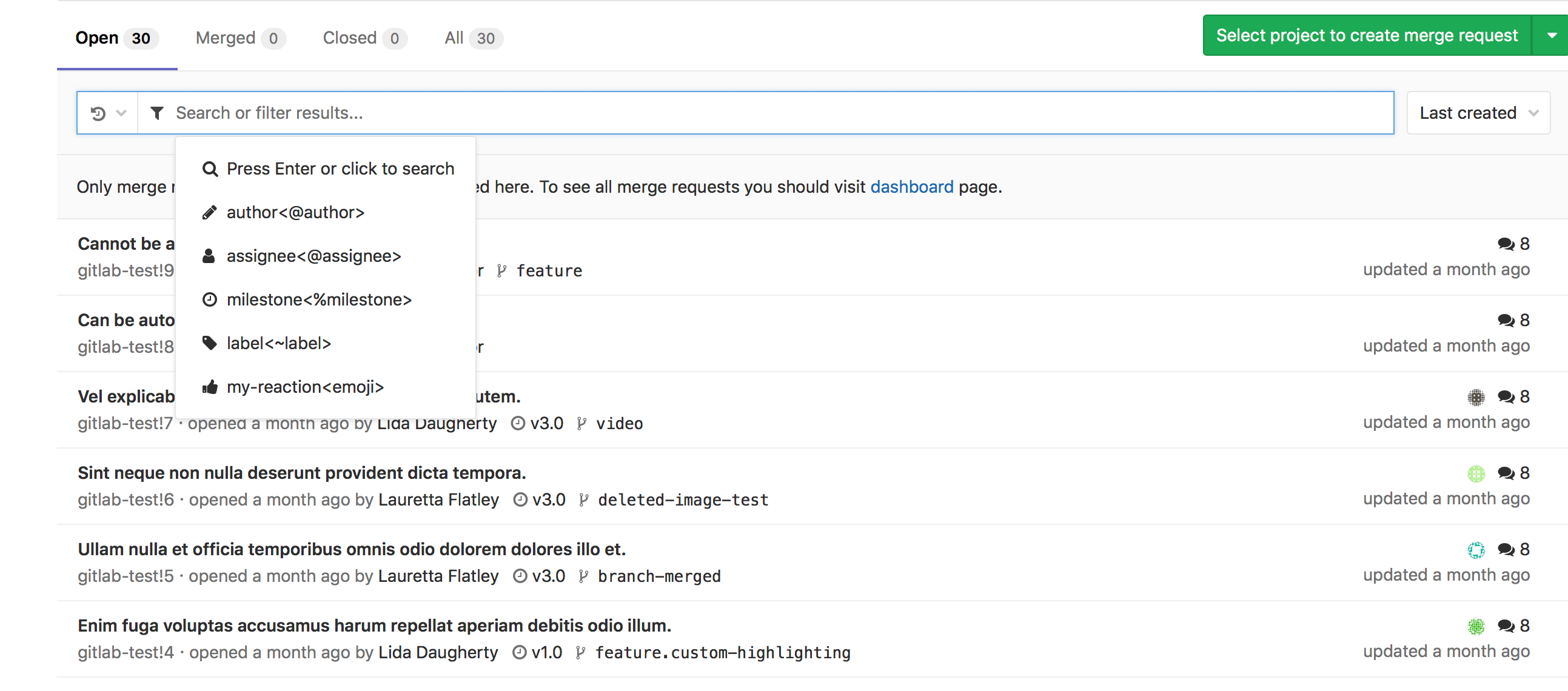
View merge requests for all projects in a group
View merge requests in all projects in the group, including all projects of all descendant subgroups of the group. Navigate to Group > Merge Requests to view these merge requests. This view also has the open and closed merge requests tabs.
You can search and filter the results from here.
Semi-linear history merge requests
A merge commit is created for every merge, but the branch is only merged if a fast-forward merge is possible. This ensures that if the merge request build succeeded, the target branch build will also succeed after merging.
Navigate to a project's settings, select the Merge commit with semi-linear history option under Merge Requests: Merge method and save your changes.
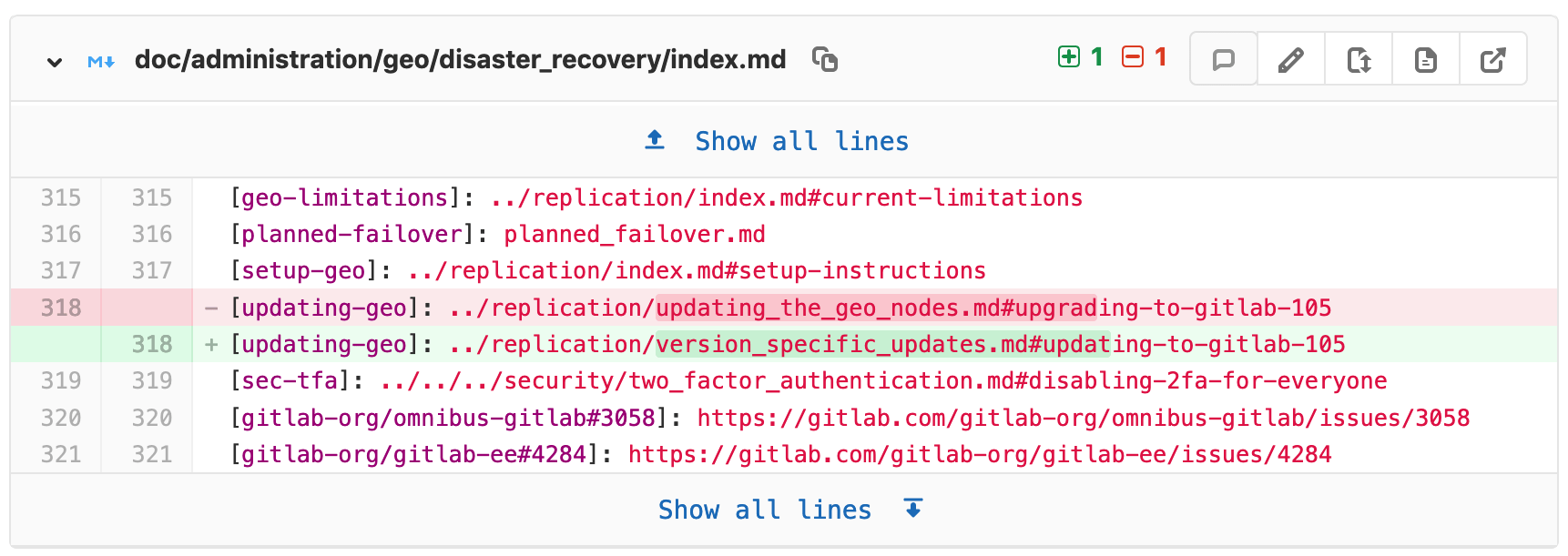
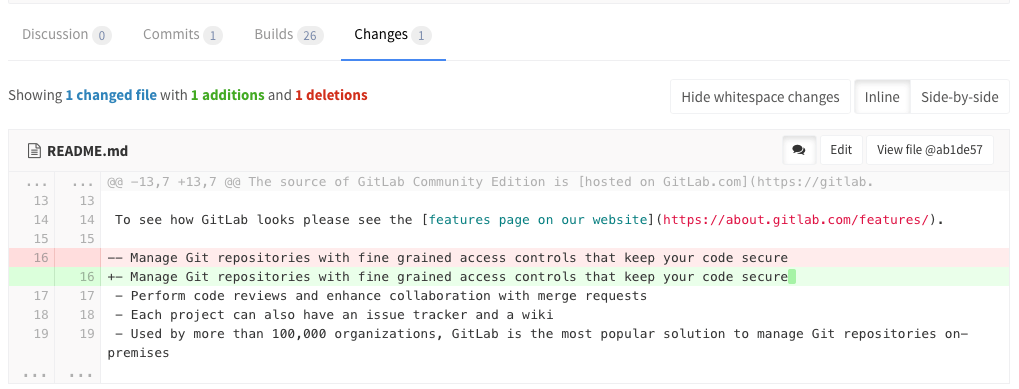
View changes between file versions
The Changes tab, below the main merge request details and next to the discussion tab, shows the changes to files between branches or commits. This view of changes to a file is also known as a diff. By default, the diff view compares the file in the merge request branch and the file in the target branch.
The diff view includes the following:
- The file's name and path.
- The number of lines added and deleted.
- Buttons for the following options:
- Toggle comments for this file; useful for inline reviews.
- Edit the file in the merge request's branch.
- Show full file, in case you want to look at the changes in context with the rest of the file.
- View file at the current commit.
- Preview the changes with Review Apps.
- The changed lines, with the specific changes highlighted.
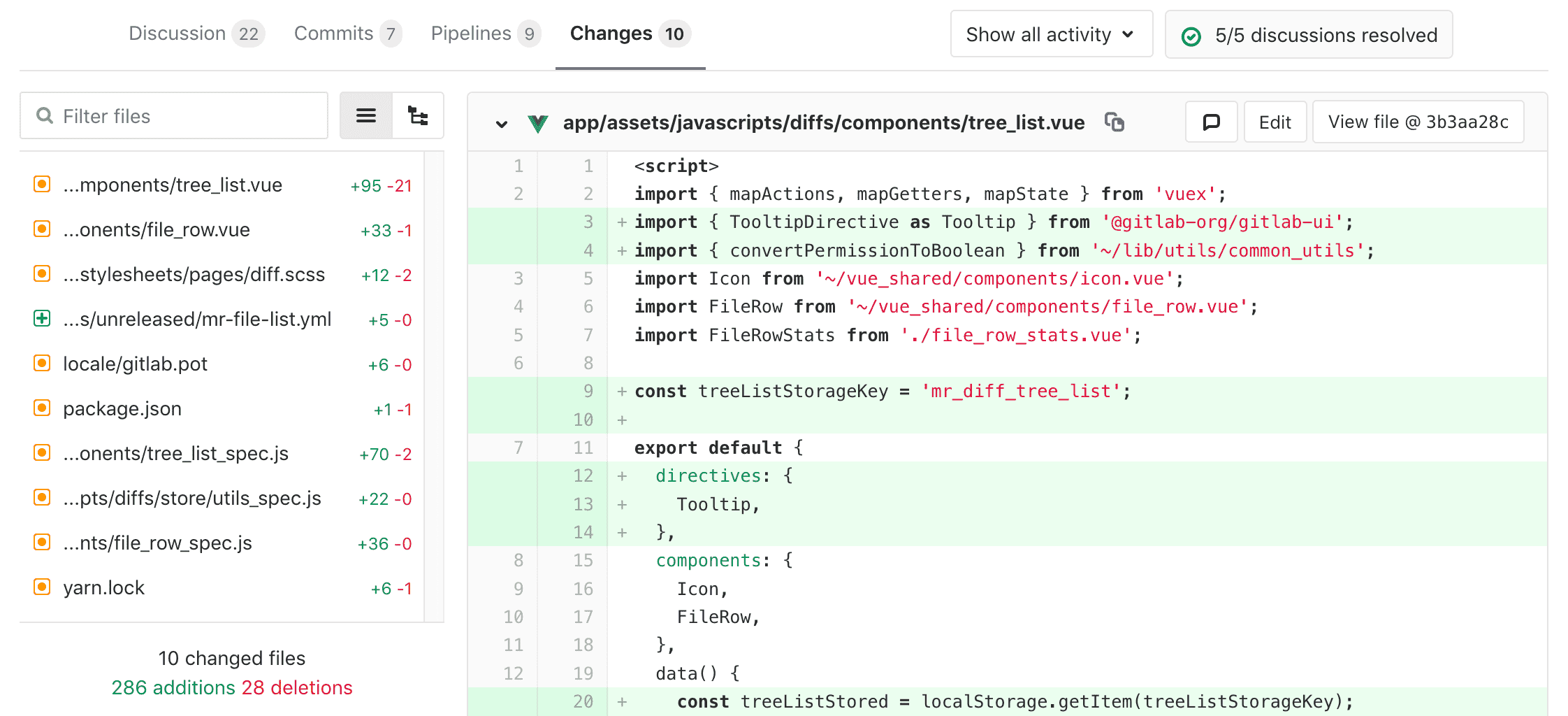
Merge request diff file navigation
When reviewing changes in the Changes tab the diff can be navigated using the file tree or file list. As you scroll through large diffs with many changes, you can quickly jump to any changed file using the file tree or file list.
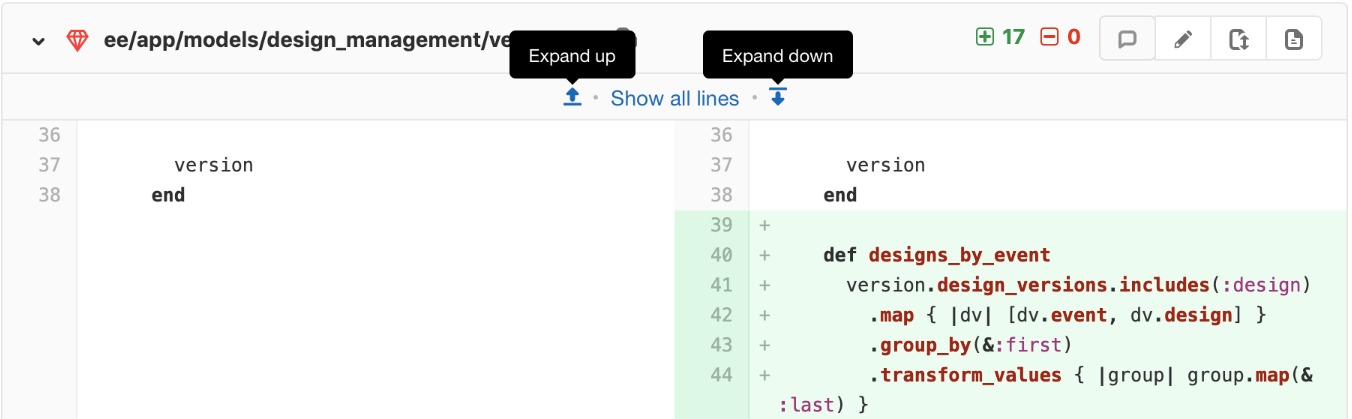
Incrementally expand merge request diffs
By default, the diff shows only the parts of a file which are changed. To view more unchanged lines above or below a change click on the Expand up or Expand down icons. You can also click on Show unchanged lines to expand the entire file.
Ignore whitespace changes in Merge Request diff view
If you click the Hide whitespace changes button, you can see the diff without whitespace changes (if there are any). This is also working when on a specific commit page.
Tip: You can append
?w=1while on the diffs page of a merge request to ignore any whitespace changes.
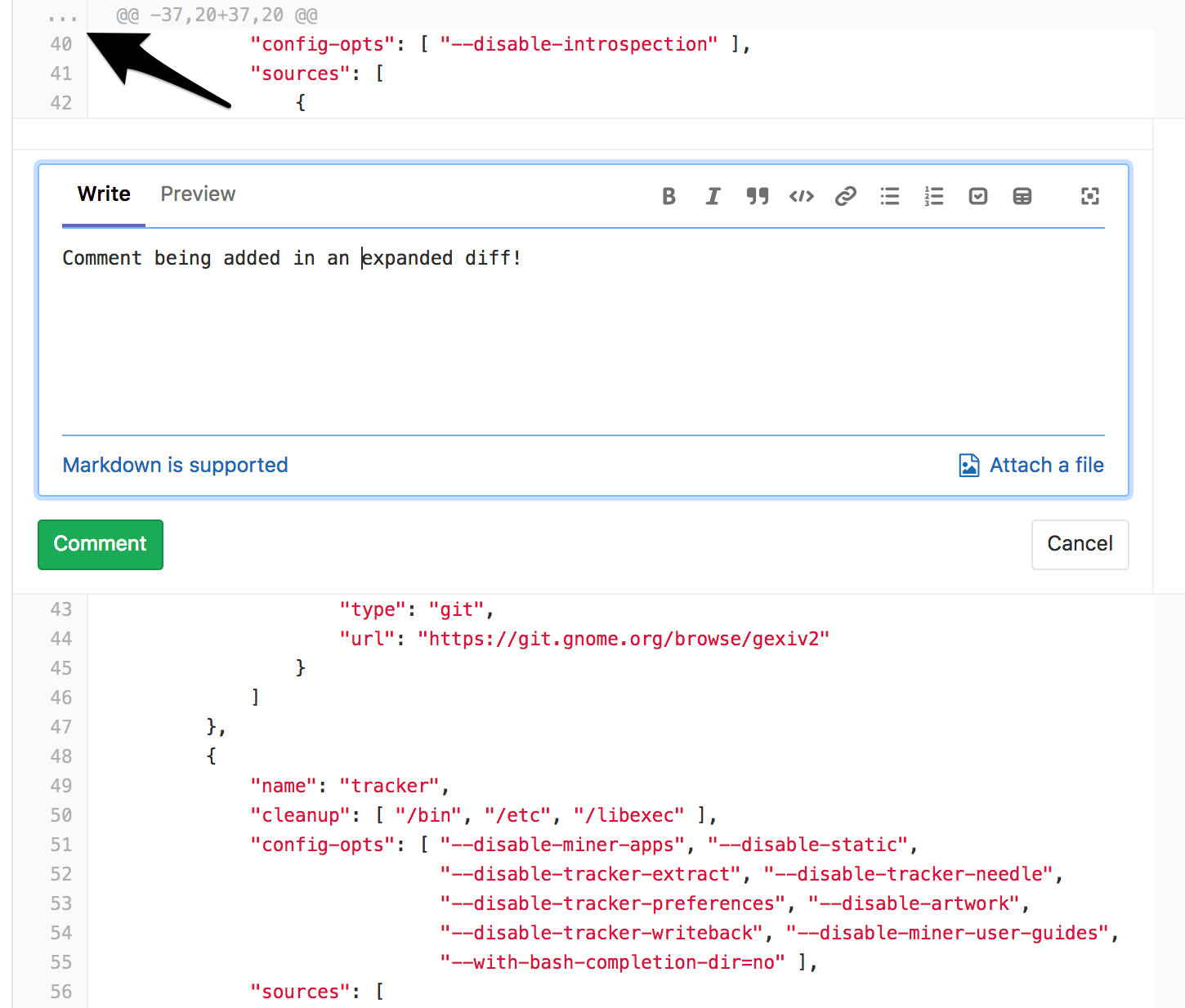
Perform inline code reviews
Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
GitLab provides a way of leaving comments in any part of the file being changed in a Merge Request. To do so, click the ... button in the gutter of the Merge Request diff UI to expand the diff lines and leave a comment, just as you would for a changed line.
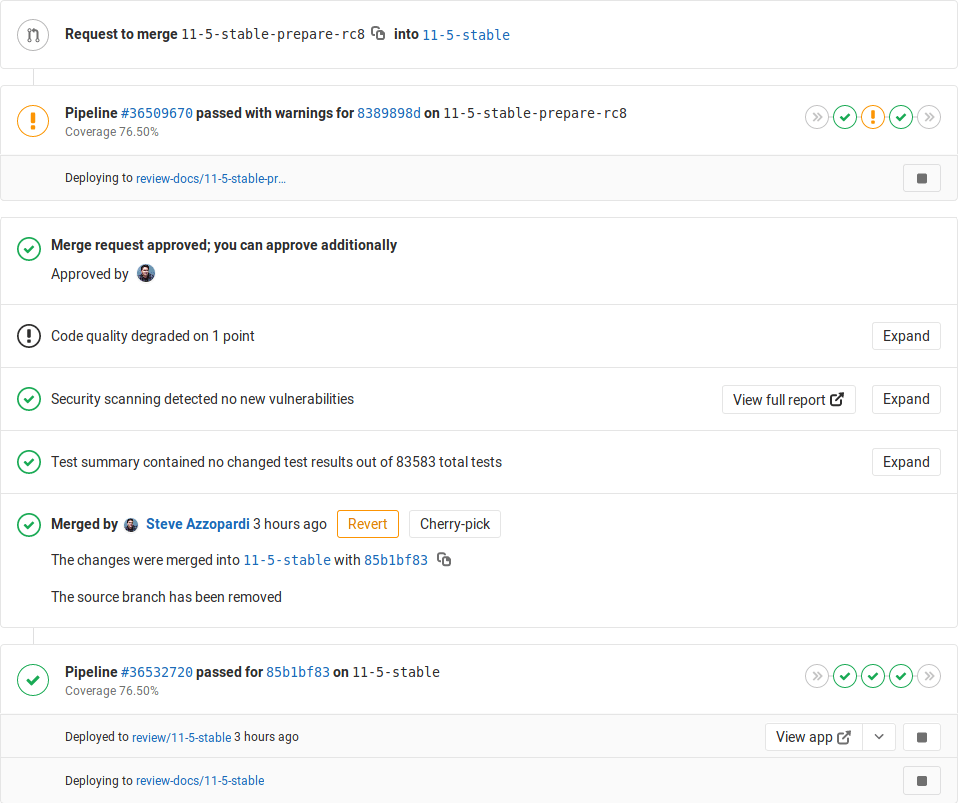
Pipeline status in merge requests widgets
If you've set up GitLab CI/CD in your project, you will be able to see:
- Both pre and post-merge pipelines and the environment information if any.
- Which deployments are in progress.
If there's an environment and the application is successfully deployed to it, the deployed environment and the link to the Review App will be shown as well.
Post-merge pipeline status
When a merge request is merged, you can see the post-merge pipeline status of the branch the merge request was merged into. For example, when a merge request is merged into the master branch and then triggers a deployment to the staging environment.
Deployments that are ongoing will be shown, as well as the deploying/deployed state
for environments. If it's the first time the branch is deployed, the link
will return a 404 error until done. During the deployment, the stop button will
be disabled. If the pipeline fails to deploy, the deployment info will be hidden.
For more information, read about pipelines.
Merge when pipeline succeeds (MWPS)
Set a merge request that looks ready to merge to merge automatically when CI pipeline succeeds.
Live preview with Review Apps
If you configured Review Apps for your project, you can preview the changes submitted to a feature-branch through a merge request in a per-branch basis. No need to checkout the branch, install and preview locally; all your changes will be available to preview by anyone with the Review Apps link.
With GitLab's Route Maps set, the merge request widget takes you directly to the pages changed, making it easier and faster to preview proposed modifications.
Associated features
There is also a large number of features to associated to merge requests:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Bulk editing merge requests | Update the attributes of multiple merge requests simultaneously. |
| Cherry-pick changes | Cherry-pick any commit in the UI by simply clicking the Cherry-pick button in a merged merge requests or a commit. |
| Fast-forward merge requests | For a linear Git history and a way to accept merge requests without creating merge commits |
| Find the merge request that introduced a change | When viewing the commit details page, GitLab will link to the merge request(s) containing that commit. |
| Merge requests versions | Select and compare the different versions of merge request diffs |
| Resolve conflicts | GitLab can provide the option to resolve certain merge request conflicts in the GitLab UI. |
| Revert changes | Revert changes from any commit from within a merge request. |
Troubleshooting
Sometimes things don't go as expected in a merge request, here are some troubleshooting steps.
Merge request cannot retrieve the pipeline status
This can occur if Sidekiq doesn't pick up the changes fast enough.
Sidekiq
Sidekiq didn't process the CI state change fast enough. Please wait a few seconds and the status will update automatically.
Bug
Merge Request pipeline statuses can't be retrieved when the following occurs:
- A Merge Request is created
- The Merge Request is closed
- Changes are made in the project
- The Merge Request is reopened
To enable the pipeline status to be properly retrieved, close and reopen the Merge Request again.
Tips
Here are some tips that will help you be more efficient with merge requests in the command line.
Note: This section might move in its own document in the future.
Checkout merge requests locally
A merge request contains all the history from a repository, plus the additional commits added to the branch associated with the merge request. Here's a few tricks to checkout a merge request locally.
Please note that you can checkout a merge request locally even if the source project is a fork (even a private fork) of the target project.
Checkout locally by adding a Git alias
Add the following alias to your ~/.gitconfig:
[alias]
mr = !sh -c 'git fetch $1 merge-requests/$2/head:mr-$1-$2 && git checkout mr-$1-$2' -Now you can check out a particular merge request from any repository and any
remote. For example, to check out the merge request with ID 5 as shown in GitLab
from the origin remote, do:
git mr origin 5This will fetch the merge request into a local mr-origin-5 branch and check
it out.
Checkout locally by modifying .git/config for a given repository
Locate the section for your GitLab remote in the .git/config file. It looks
like this:
[remote "origin"]
url = https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*You can open the file with:
git config -eNow add the following line to the above section:
fetch = +refs/merge-requests/*/head:refs/remotes/origin/merge-requests/*In the end, it should look like this:
[remote "origin"]
url = https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
fetch = +refs/merge-requests/*/head:refs/remotes/origin/merge-requests/*Now you can fetch all the merge requests:
git fetch origin
...
From https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git
* [new ref] refs/merge-requests/1/head -> origin/merge-requests/1
* [new ref] refs/merge-requests/2/head -> origin/merge-requests/2
...And to check out a particular merge request:
git checkout origin/merge-requests/1All the above can be done with the git-mr script.